Previous
Your First Project
Goal: Get a computer vision pipeline working.
Skills: Connect a machine to Viam, configure components in the Viam UI, configure services in the Viam UI.
Time: ~15 min
Before starting this tutorial, you need the can inspection simulation running. Follow the Gazebo Simulation Setup Guide to:
Once you see “Can Inspection Simulation Running!” in the container logs and your machine shows Live in the Viam app, return here to continue.
The simulation runs Gazebo Harmonic inside a Docker container. It simulates a conveyor belt with cans (some dented) passing under an inspection camera. viam-server runs on the Linux virtual machine inside the container and connects to Viam’s cloud, just like it would on a physical machine. Everything you configure in the Viam app applies to the simulated hardware.
In the Viam app, make sure the Configure tab for your machine is selected.
Your machine is online but empty. To configure it, you’ll add components and services to your machine part. A machine part is the compute hardware for your robot. In this tutorial, your machine part is a virtual machine running Linux in the Docker container.
Find inspection-station-1-main in the Configure tab.
You’ll now add the camera as a component.
To add the camera component to your machine part:
gz-cameragz-camera:rgb-camerainspection-cam for the name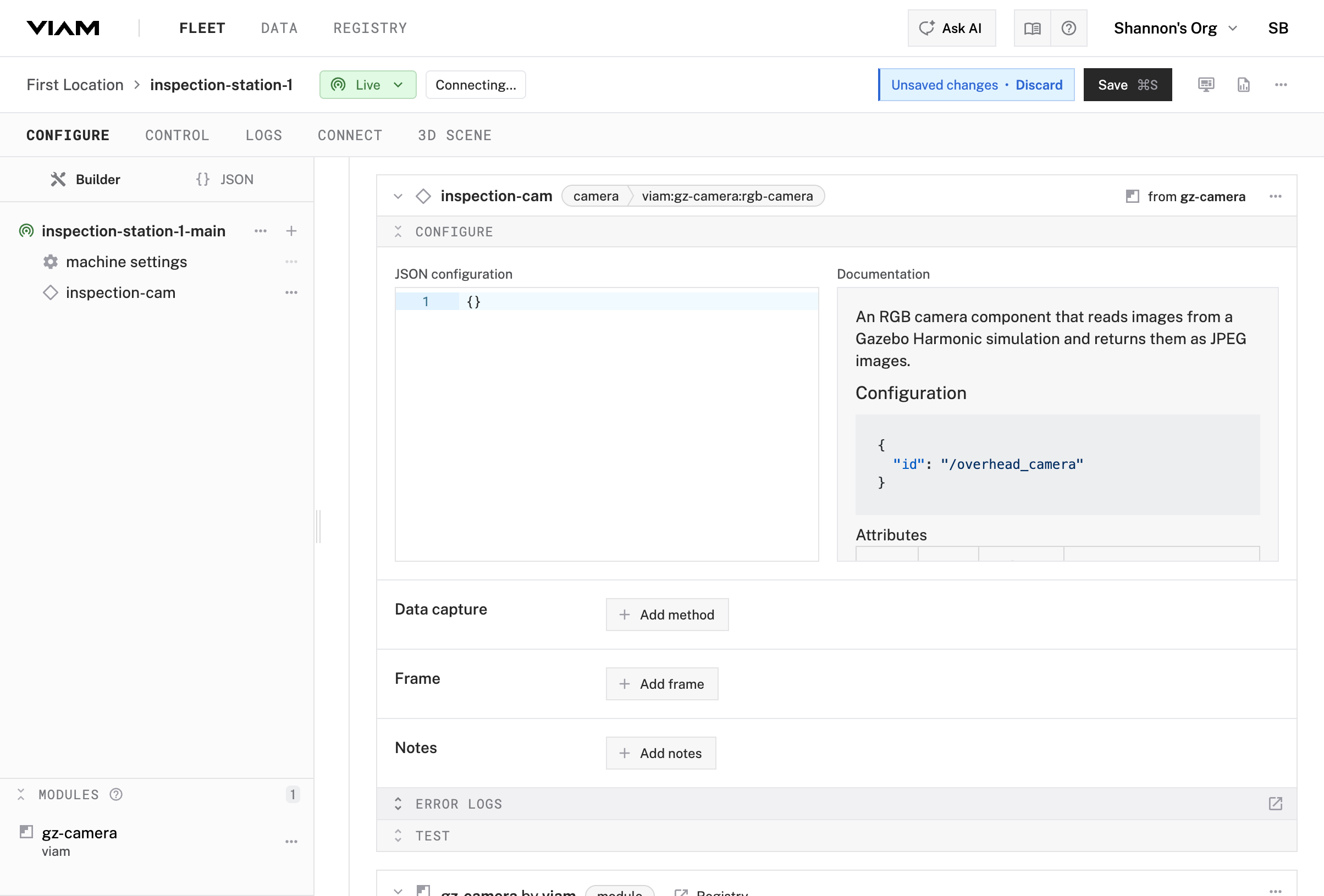
To configure your camera component to work with the camera in the simulation, you need to specify the correct camera ID. Most components require a few configuration parameters.
In the JSON Configuration section, add:
{
"id": "/inspection_camera"
}
Click Save in the top right
You declared “this machine has an attached camera called inspection-cam” by editing the configuration in the Viam app.
When you clicked Save, viam-server loaded the camera module which implements the camera API for the specific model of camera we are using.
It also added a camera component, and made the camera available through Viam’s standard camera API.
Software you write, other services, and user interface components will use the API to get the images they need.
Using the API as an abstraction means that everything still works if you swap cameras.
Verify the camera is working. Every component in Viam has a built-in test card right in the configuration view.
inspection-cam selectedThe camera component test card uses the camera API to add an image feed to the Viam app, enabling you to determine whether your camera is working. You should see a live video feed from the simulated camera. This is an overhead view of the conveyor/staging area.
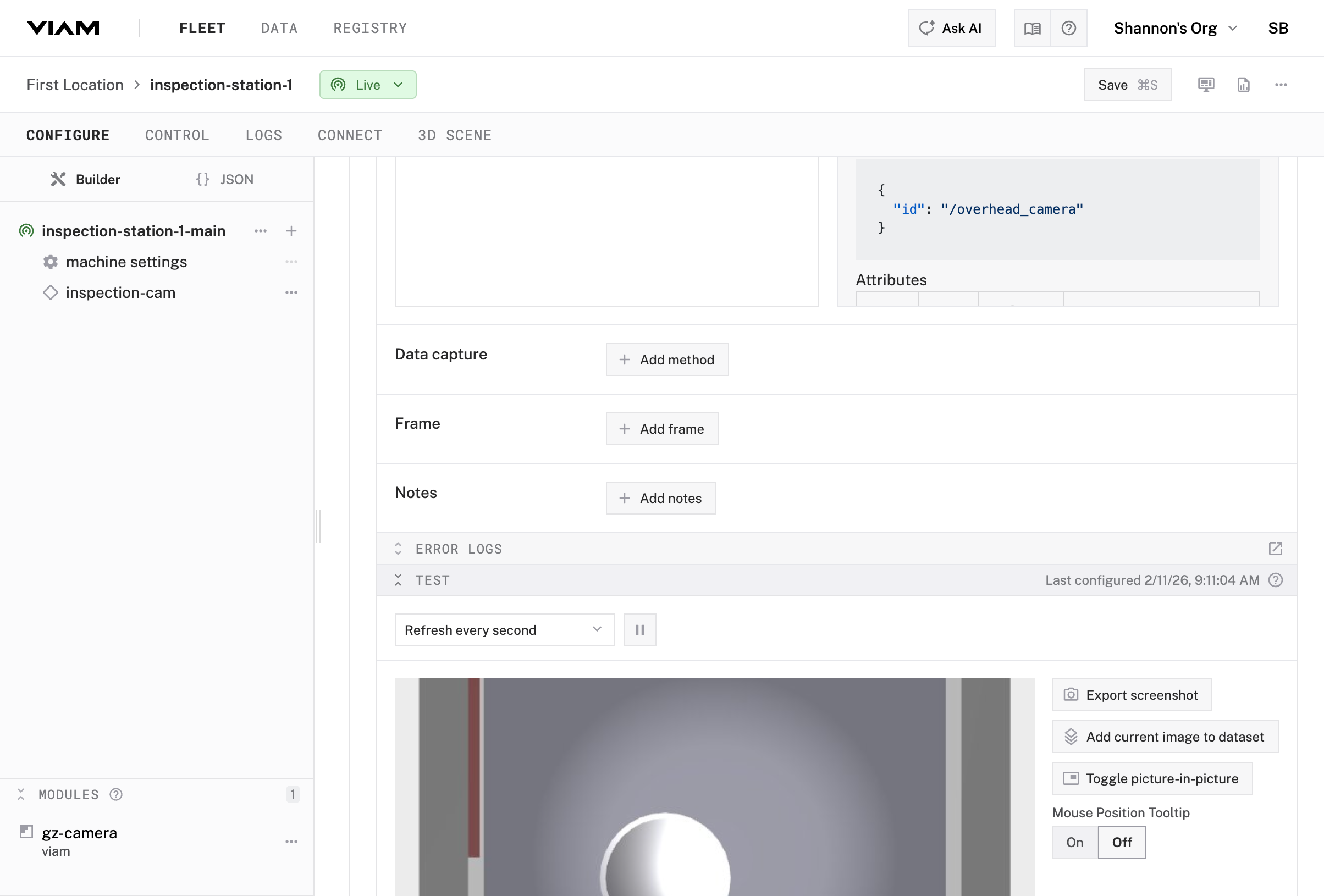
Your camera is working. You can stream video and capture images from the simulated inspection station.
Now you’ll add machine learning to run inference on your camera feed. You’ll configure two services:
tflitetflight_cpu/tflight_cpumodel-service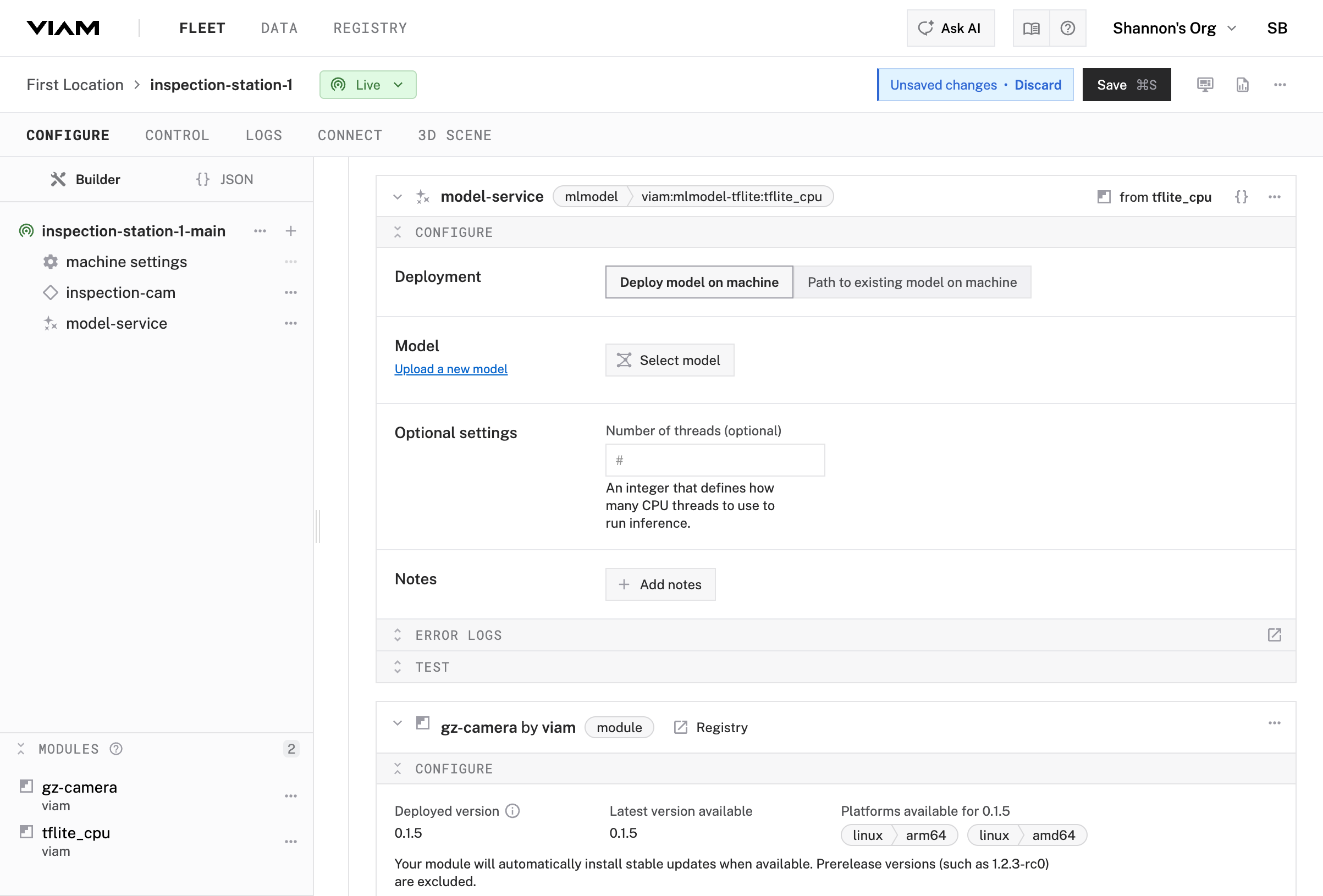
Configure the model-service ML model service you just included in your configuration.
In the model-service configuration panel, click Select model
Search for can-defect-detection and select it from the list (a model that classifies cans as PASS or FAIL based on defect detection)
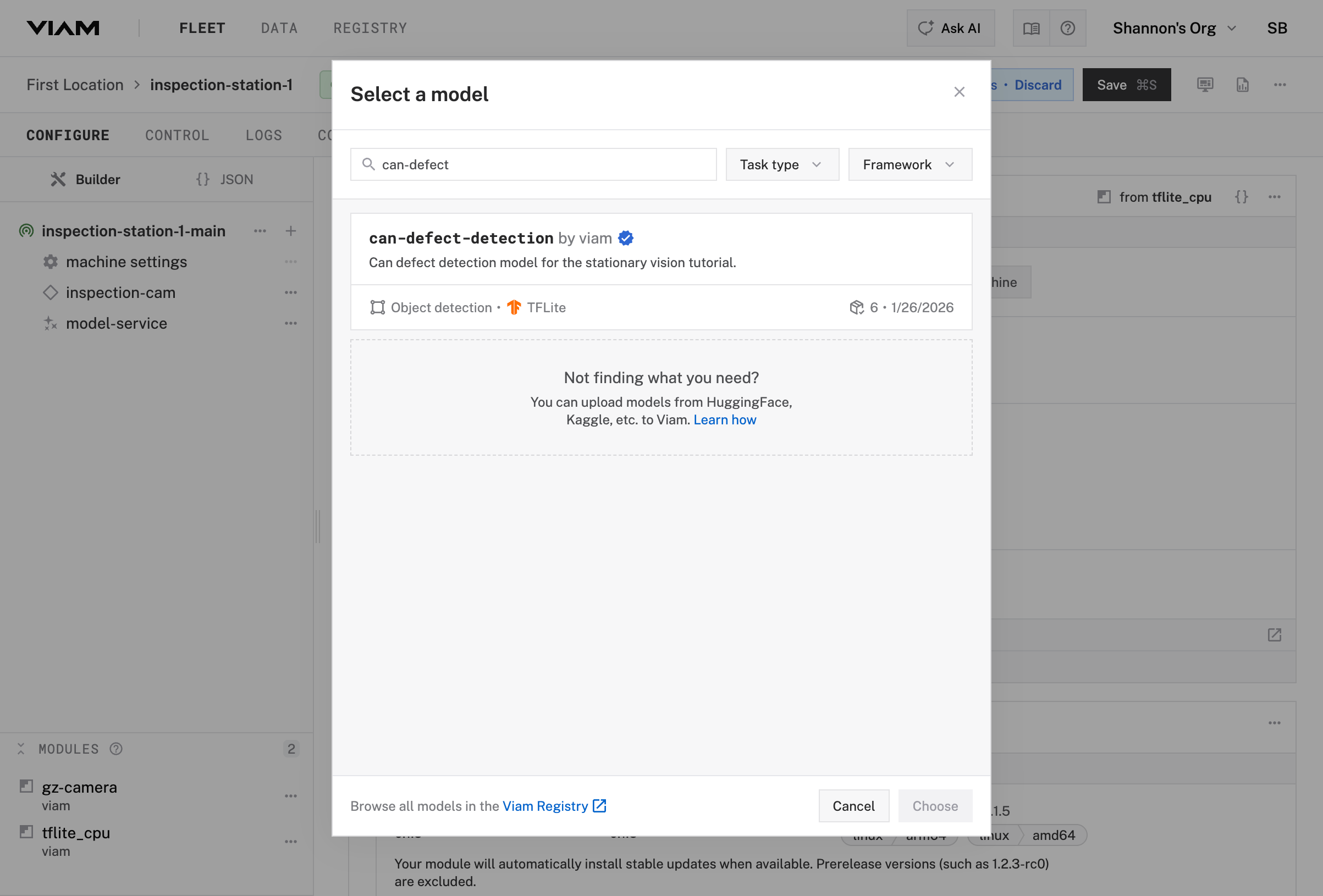
Click Choose to save the model selection
Click Save in the upper right corner to save your configuration
For a different application, you’d train a model on your specific data and upload it to the registry. The registry handles versioning and deployment of ML models across your fleet.
Now add a vision service that connects your camera to the ML model service.
visionvision-service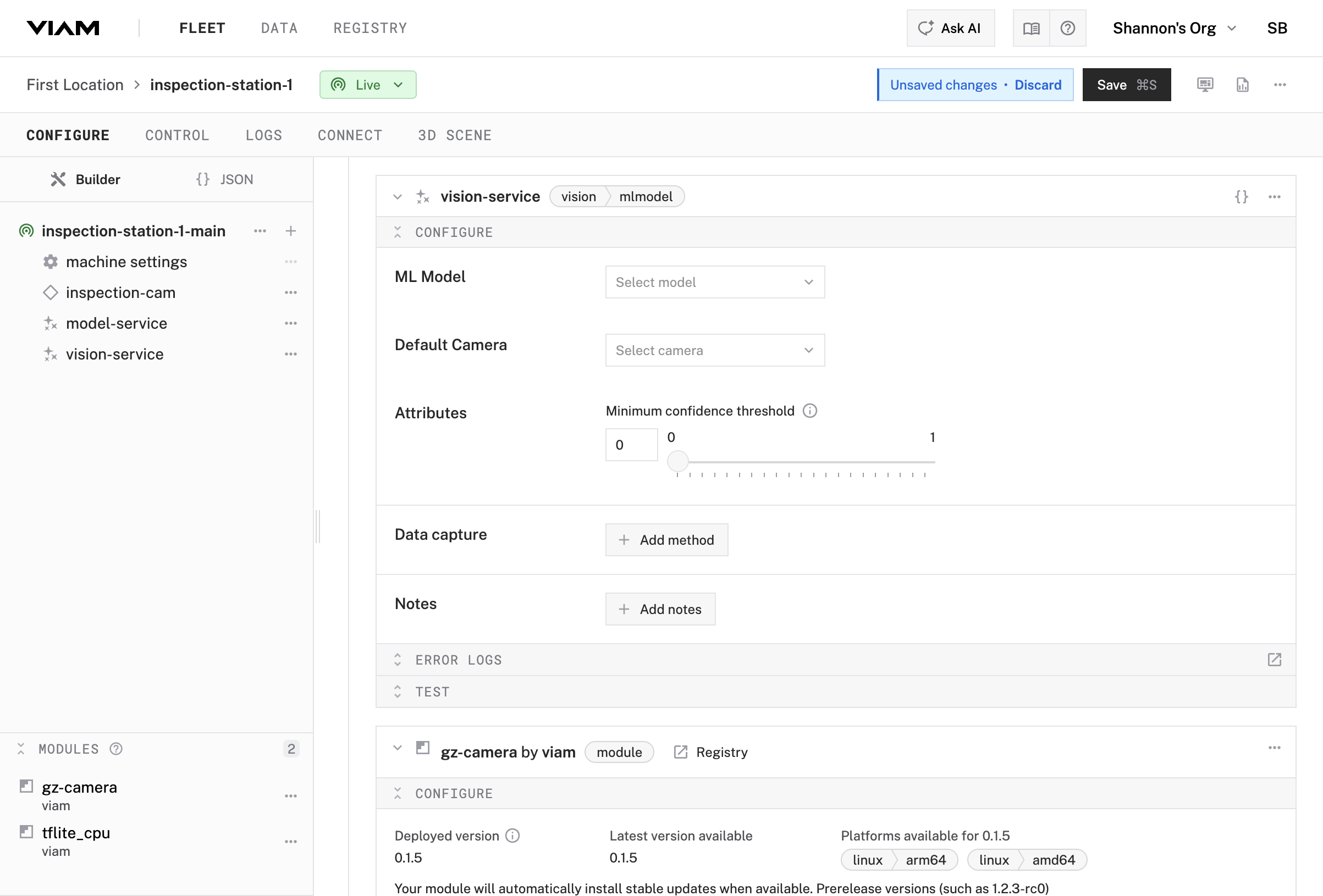
vision-service service in your machine’s configurationmodel-service (the ML model service you just created)inspection-cam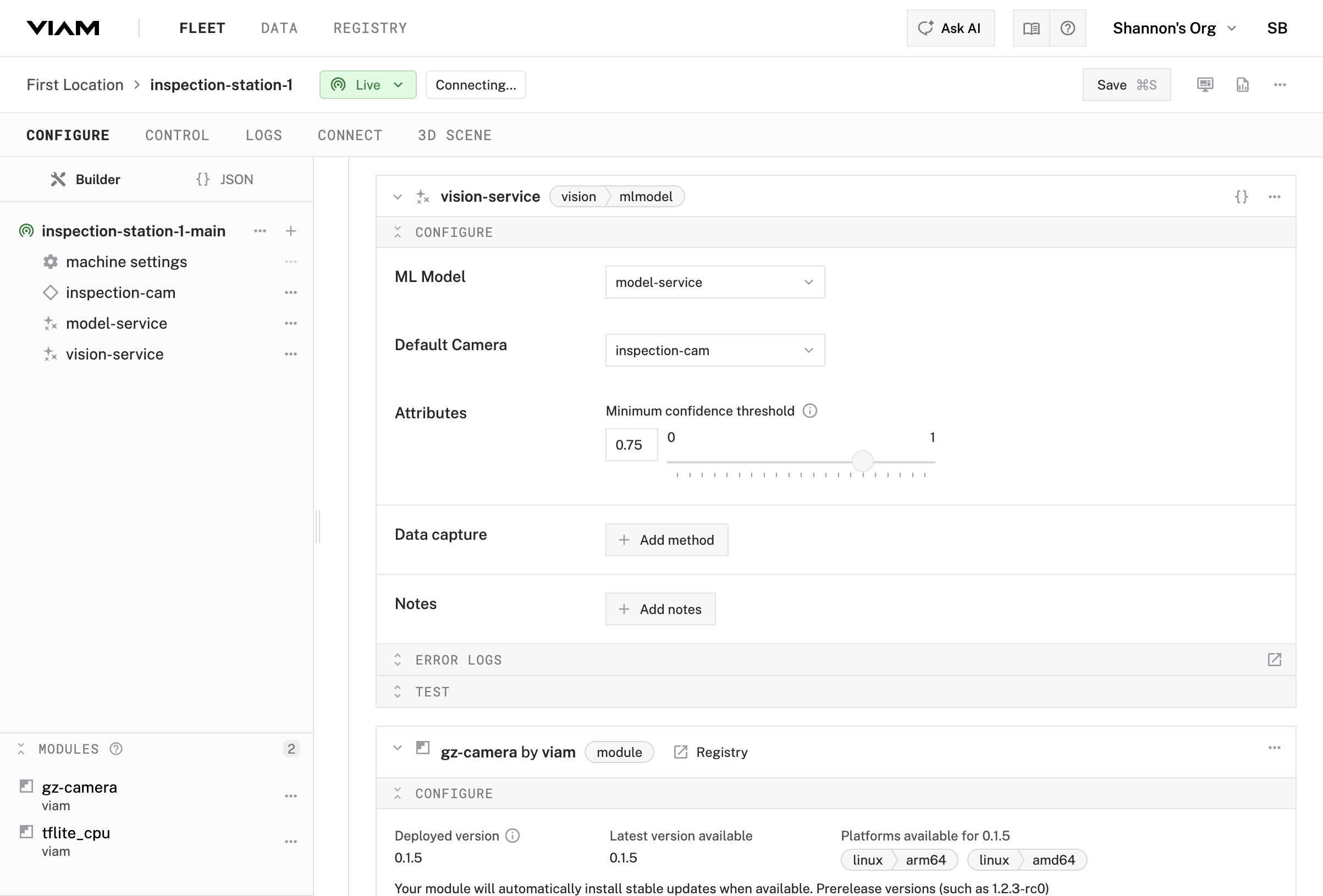
vision-service configuration panelinspection-cam as the camera sourceLive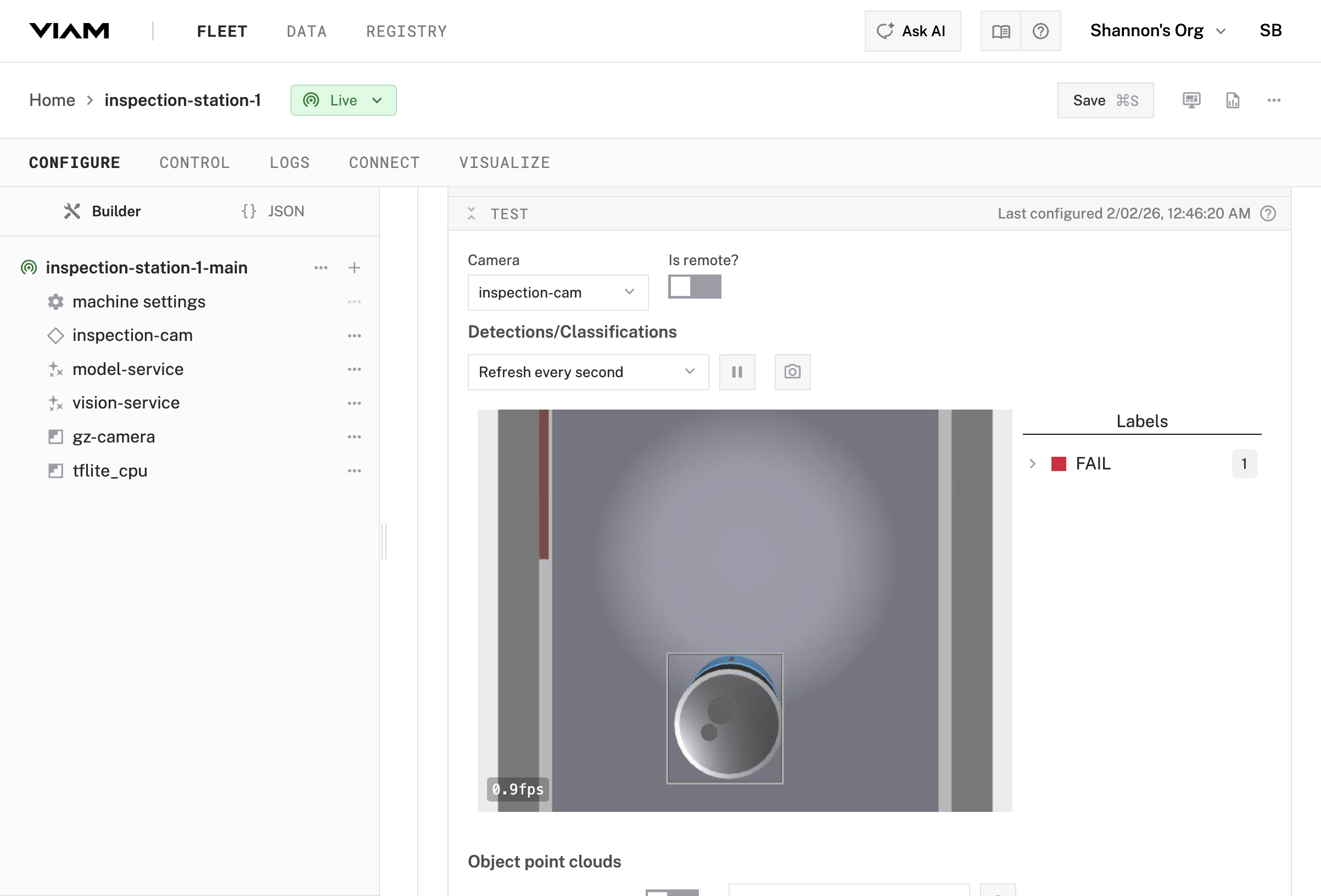
You’ve configured a complete ML inference pipeline that can detect defective cans.
The ML model service loads a trained model and exposes an Infer() method, while the vision service handles the rest—grabbing images from the camera, running them through the model, and returning structured detections with bounding boxes, labels, and confidence scores.
This pattern works for any ML task. Swap the model for object detection, classification, or segmentation without changing the pipeline. You can also swap one camera for another with one configuration change.
Next, you’ll set up continuous data capture so every detection is recorded and queryable.
Continue to Part 2: Data Capture →
Was this page helpful?
Glad to hear it! If you have any other feedback please let us know:
We're sorry about that. To help us improve, please tell us what we can do better:
Thank you!